Neodymium, Nd, atomic number 60
Neodymium usage, Neodymium extraction, Neodymium prices
General
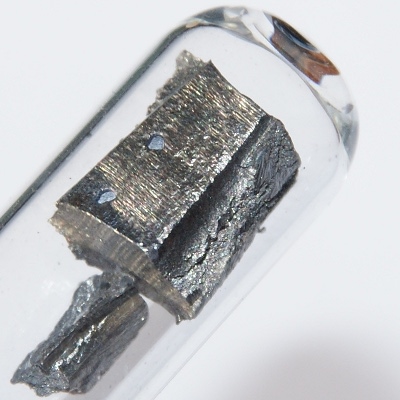
Neodymium (nomenclature recommendation was temporarily: neodymium) is a chemical element with the element symbol Nd and the atomic number 60. In the periodic table it is in the group of lanthanides and thus also belongs to the metals of the rare earths. The element name derives from the Greek words νέος neos for "new" and δίδυμος didymos for "twin" (as a twin of Lanthan) from.
The metal is mainly used for strong magnets. Neodymium was isolated together with praseodymium 1885 by Carl F. Auer von Welsbach from Didym discovered by Carl Gustav Mosander. Pure metallic neodymium was first presented to 1925.
Neodymium occurs naturally only in chemical compounds associated with other lanthanides, preferably minerals:
Monazite (Ce, La, Th, Nd, Y) PO4
Bastnaesite ((Ce, La, Th, Nd, Y) (CO3) F)
Mischmetal contains up to 18% Neodymium.
The most important supplier with 97% of world production is China. That leads to considerable environmental problems there. “When the neodymium is separated from the extracted rock, poisonous waste products are created, and radioactive uranium and thorium are released during the mining process. At least some of these substances end up in the groundwater, contaminate fauna and flora considerably and are classified as harmful to human health, ”reports the ARD television magazine Panorama.
Other economically exploitable deposits can be found in Australia.
Recovery
After an elaborate separation of the neodymium components, the oxide is converted to neodymium fluoride with hydrogen fluoride and then reduced to neodymium with calcium to form calcium fluoride. Calcium residues and impurities are separated in a remelting process in a vacuum.
2011 researched for the NDR that the production, which is mainly used in China, generates enormous environmental damage through the release of toxic waste and radioactive waste.
The production by electrolysis of Neodymhalogeniden is rarely used today.
Features
The silvery-white shiny metal belongs to the lanthanides and metals of the rare earths. It is somewhat more resistant to corrosion in the air than europium, lanthanum, cerium or praseodymium, but easily forms a pink-violet oxide layer that can peel off in the air. At high temperatures it burns to the sesquioxide Nd2O3.
It reacts with water to form neodymium hydroxide Nd (OH) 3 with formation of hydrogen. Hydrogen converts to the hydride NdH2. In addition to the main value / oxidation number 3, the oxide
2 and 4.
Usage
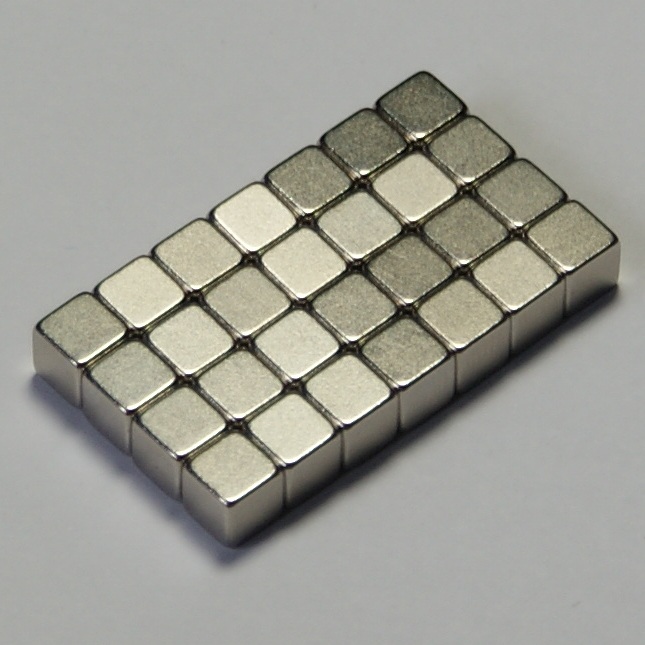
Neodymium-iron-boron compounds for the production of strongest magnets. They are used for magnetic resonance tomographs, micromotors and hard disks (positioning of the read / write heads), permanent magnet rotors (eg stepper and servo motors, efficient permanent magnet DC machines, eg in some wind turbine types, for the propulsion of electric and hybrid vehicles as well as model vehicles). Drives), linear motors for positioning axes, eg B. CNC machines, high quality speakers and headphones. Compared to the samarium cobalt magnets, they are stronger and much cheaper, but also much more sensitive to heat. Neodymium salts for coloring enamel
Blue porcelain color
Neodymium (III) oxide for glass staining. It produces very warm violet to maroon and gray tones. Such glasses have sharp absorption bands and are used in astronomy for calibration.
Discoloration of ferrous glass
UV-absorbing glasses (solar control glass)
Part of the industrially widespread neodymium-YAG laser
Neodymium oxide doped barium titanate for capacitor dielectrics
Because of its pyrophoric properties also as alloying partner with cerium in flint stones
For the preparation of neodymium-catalyzed polybutadiene rubber (Nd-PBR)
Neodymium Iron Boron (Nd2Fe14B) is currently the strongest material for
Permanent magnets. You can achieve a remanence of up to 1,4 Tesla. The coercive force jHc varies in the range from 870 to 2750 kA / m.
| General | |
| Name, symbolOrder number | Neodymium, Nd, 60 |
| Series | lanthanides |
| Group, period, block | La, 6, f |
| Appearance | silvery white, yellowish |
| CAS number | 7440-00-8 |
| Mass fraction of the earth's envelope | 22 ppm |
| Atomic | |
| atomic mass | 144,24 u |
| atomic radius | 185 pm |
| Covalent radius | 201 pm |
| Elektronenkonf. | [Xe] 4f (4) 6s2 |
| 1. ionization | 533,1 KJ / mol |
| 2. ionization | 1040 KJ / mol |
| 3. ionization | 2130 KJ / mol |
| Physically | |
| Physical state | fixed |
| crystal structure | hexagonal |
| density | 7,003 g / cm3 (25 ° C) |
| magnetism | paramagnetic (χm = 3,6 * 10 (-3)) |
| melting point | 1297 K (1024 C) |
| boiling point | 3373 K (3100 C) |
| Molar volume | 20,59 * 10 (-6) m (3) / mol |
| Heat of vaporization | 285 KJ / mol |
| heat of fusion | 7,1 KJ / mol |
| Electric conductivity | 1,56 * 10 (6) A / (V * m) |
| thermal conductivity | 17 W / (m * K) |
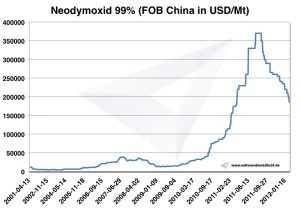
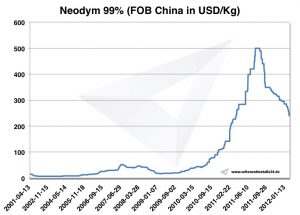
Neodymium prices
Prices for neodymium -> prices for rare earths