Praseodymium, Pr, atomic number 59
General
Praseodymium is a chemical element with the element symbol Pr and the atomic number 59. In the periodic table it is in the group of lanthanides and thus also belongs to the metals of the rare earths. From the green color of its compounds comes the name: the Greek word prásinos means "leek green", didymos "double" or "twin".
1841 Carl Gustav Mosander extracted the rare earth Didym from lanthanum oxide. 1874 remarked to Per Teodor Cleve that Didym was actually two elements. In the year 1879 Lecoq de Boisbaudran samarium isolated from Didym, which he won from the mineral Samarskit. 1885 managed to separate Carl Auer von Welsbach, Didym in Praseodymium and Neodymium, which form both salts of different colors.
Praseodymium is a companion in the typical rare earth minerals Cerit, Monazit and Bastnäsit. The worldwide reserves are estimated at 4 million tons.
Recovery
As with all lanthanides, the ores are first enriched by flotation, then the metals are converted to corresponding halides and separated by fractional crystallization, ion exchange or extraction. The metal is obtained by fused-salt electrolysis or calcium reduction.
Features
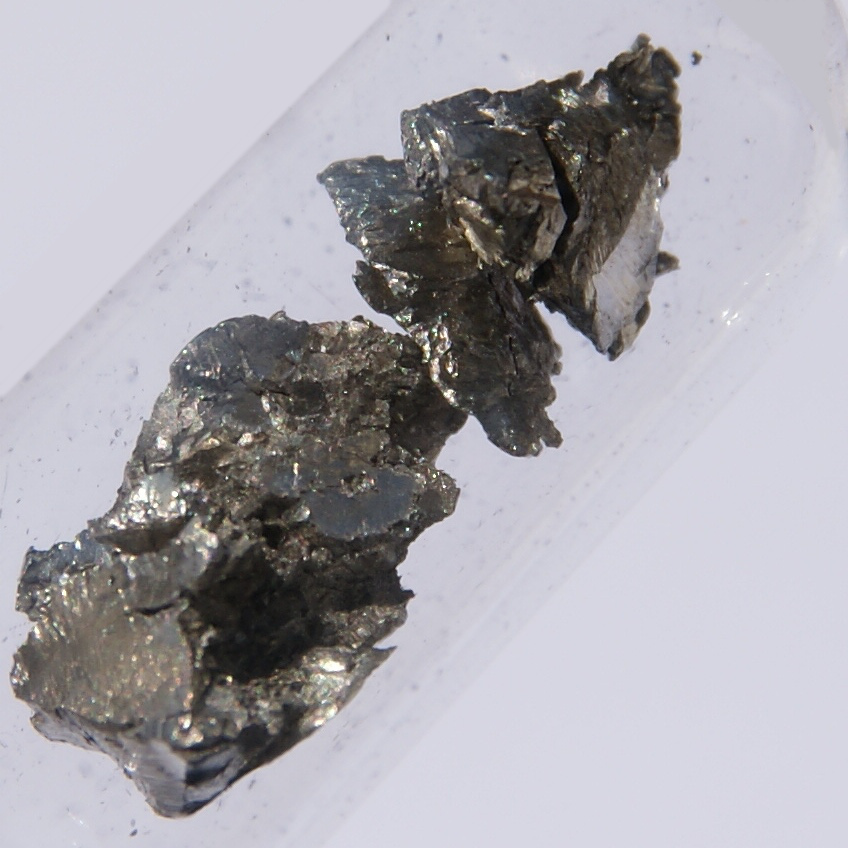
Praseodymium is a soft, silver-white paramagnetic metal, which belongs to the lanthanides and rare earth metals. It is somewhat more corrosion-resistant in air than europium, lanthanum or cerium, but easily forms a green oxide layer that flakes off in air. At 798 ° C, the hexagonal α-Pr converts to the body-centered cubic β-Pr. Natural praseodymium consists only of the stable isotope 141Pr. 38 other radioactive isotopes are known, with 143Pr and 142Pr being the longest-lived, with half-lives of 13,57 days and 19,12 hours, respectively. All other isotopes have half-lives of less than 5,985 hours, most even less than 33 seconds. There are also 6 metastable states, with 138mPr (t½ 2,12 hours), 142mPr (t½ 14,6 minutes) and 134mPr (t½ 11 minutes) being the most stable.
The isotopes have an atomic mass range of 120,955 (121Pr) to 158,955 (159Pr). Because of its sensitivity to air, praseodymium should be stored under gasoline or sealed in plastic or glass.
A biological significance is not known, but praseodymium compounds are said to be slightly liver damaging. However, there are no toxicity values.
Praseodymium occurs in its compounds trivalent and tetravalent, with the trivalent oxidation number being the more abundant. Pr (III) ions are yellow-green, and Pr (IV) ions are colorless. Under particular reductive conditions and divalent praseodymium can be realized, for. Eg in Pr2I5.
Several halides of all stages are known, for example PrF3, PrF4, PrCl3, PrBr3, PrI3, Pr2I5. The trivalent halides form different hydrates.
There are also various compounds with chalcogens: the normal brown-black praseodymium (III, IV) oxide Pr6O11, the almost black PrO2, the green Pr2O3, Pr2S3, Pr2Te3 and other binary compounds such as PrN, PrP. In addition, praseodymium is present in various salts, such as the hygroscopic praseodymium nitrate Pr (NO3) 3.xH2O, the beautifully crystallizing praseodymium sulfate Pr2 (SO4) 2.8 H2O, and others.
In addition, it forms several fluorido complexes such. For example, the K2 [PrF6] with quadrivalent Pr.
Usage
Praseodymium is used in alloys with magnesium for the production of high-strength metal for aircraft engines.
Cobalt and iron alloys are strong permanent magnets.
Praseodymium compounds are used for coloring glass and enamel (for example in green-colored headlamp lenses in lighting technology).
The compounds also improve UV absorption and are used for eye protection glasses during welding.
| General | |
| Name, symbol
ordinal |
Praseodymium, Pr, 59 |
| Series | lanthanides |
| Group, period, block | La, 6, f |
| Appearance | silvery white, yellowish |
| CAS number | 7440-10-0 |
| Mass fraction of the earth's envelope | 5,2 ppm |
| Atomic | |
| atomic mass | 140,90765 u |
| atomic radius | 185 pm |
| Covalent radius | 203 pm |
| Elektronenkonf. | [Xe] 4f (3) 6s2 |
| 1. ionization | 527,0 KJ / mol |
| 2. ionization | 1020 KJ / mol |
| 3. ionization | 2086 KJ / mol |
| Physically | |
| Physical state | fixed |
| crystal structure | hexagonal |
| density | 6,475 g / cm3 (25 ° C) |
| magnetism | paramagnetic (χm = 2,9 * 10 (-3)) |
| melting point | 1208 K (935 C) |
| boiling point | 3563 K (3290 C) |
| Molar volume | 20,80 * 10 (-6) m (3) / mol |
| Heat of vaporization | 330 KJ / mol |
| heat of fusion | 6,9 KJ / mol |
| Electric conductivity | 1,43 * 10 (6) A / (V * m) |
| thermal conductivity | 13 W / (m * K) |
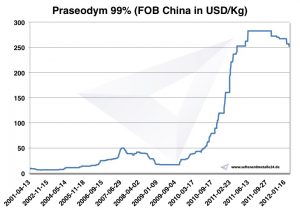
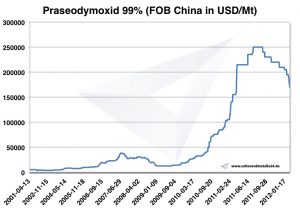
Praseodymium price
Praseodymium prices -> prices for rare earths