Ytterbium, Yb, atomic number 70
General
Ytterbium [ʏtɛrbiʊm] is a chemical element with the element symbol Yb and the ordinal number 70. In the periodic table it is in the group of lanthanides and thus also belongs to the metals of the rare earths. Ytterbium is named after the first site, the Ytterby mine near Stockholm, as well as yttrium, terbium and erbium.
Ytterbium (derived from Ytterby, a pit on an archipelago north of Stockholm, which was also the name of the elements yttrium, terbium and erbium godfather) 1878 was discovered by the Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac. Marignac found a new ingredient in the soil known as Erbia and called it Ytterbia. He suspected in the compound isolated from him a new element, which he called Ytterbium. 1907 separated French chemist Georges Urbain Marignacs Ytterbia into two components, Neoytterbia and Lutetia. Carl Auer von Welsbach also worked at the same time with Ytterbia and called the two components Aldebaranium and Cassiopeium. Later, the element name Neoytterbium was shortened to Ytterbium. The pure metal was 1937 by Klemm and Bonner represented by the reduction of YbF3 with potassium. The determination of the physical and chemical properties of the element ytterbium could only be done 1953 after production of the pure metal.

Ytterbium metal
Recovery
After extensive separation of the other ytterbium companions, the oxide is reduced with lanthanum to metallic ytterbium. Then the ytterbium is sublimated.
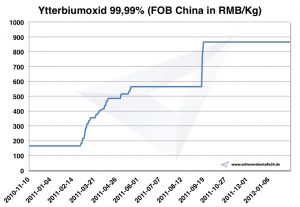
Chart Ytterbium oxide 2010-2012
Features
The silvery white metal is very elastic and soft. It forms three allotropic modifications with conversion points at -13 ° C and 795 ° C. At room temperature, β-ytterbium forms a face-centered cubic lattice, at higher temperatures a cubic-body centered lattice. At a pressure of 16.000 bar, β-Yb shows semiconductor properties in terms of electrical conductivity.
Ytterbium turns gray in dry air. At higher temperatures it burns to the sesquioxide Yb2O3. With water, it reacts slowly with evolution of hydrogen to the hydroxide. In mineral acids, it dissolves to form hydrogen. In its compounds it is usually in the oxidation number + 3 before, the Yb3 + cations form colorless solutions in water, Yb2 + cations green solutions.
Periodic Table Ytterium-70
Usage
Ytterbium can be used for grain refining and to improve the mechanical properties of stainless steels. The radioactive isotope 169Yb (half-life 32 days) is occasionally used as a source of γ-radiation in nuclear medicine.
Ytterbium-cobalt-iron-manganese alloys are suitable for high-quality permanent magnets.
Ytterbium-doped crystals (mainly Yb: YAG) are used as reinforcing material in lasers.
Ytterbium is not very toxic. Metal dusts are fire and explosive.
| General | |
| Name, symbol
ordinal |
Ytterbium, Yb, 70 |
| Series | lanthanides |
| Group, period, block | La, 6, f |
| Appearance | silvery white |
| CAS number | 7440-64-4 |
| Mass fraction of the earth's envelope | 2,5 ppm |
| Atomic | |
| atomic mass | 173,04 u |
| atomic radius | 175 pm |
| Covalent radius | 187 pm |
| Elektronenkonf. | [Xe] 4f (14) 6s2 |
| 1. ionization | 603,4 KJ / mol |
| 2. ionization | 1174,8 KJ / mol |
| 3. ionization | 2417 KJ / mol |
| Physically | |
| Physical state | fixed |
| crystal structure | Cubic area-centered |
| density | 6,973 g / cm3 (25 ° C) |
| magnetism | paramagnetic (χm = 3,4 * 10 (-5)) |
| melting point | 1097 K (824 C) |
| boiling point | 1469 K 1196 C) |
| Molar volume | 24,84 * 10 (-6) m (3) / mol |
| Heat of vaporization | 160 KJ / mol |
| heat of fusion | 7,7 KJ / mol |
| Electric conductivity | 4,0 * 10 (6) A / (V * m) |
| thermal conductivity | 39 W / (m * K) |
